The Advantages of 3D printing Polypropylene
With PP’s unique mechanical properties on the one hand, and the great design and production benefits that Additive Manufacturing builds upon, promising new possibilities are now opened up for technical parts.
Prototyping
3D printing has everything it takes to carry out prototyping processes ideally. As a flexible manufacturing technique, this technology doesn’t require part-specific tools to create them. Different prototypes can thus be iterated individually, without inducing the costs that other traditional manufacturing tools would.
Along with cost-effectiveness, Additive Manufacturing allows to iterate prototypes at a much higher pace than other processes, which is key to refining them subsequently, until the perfect version is achieved.
Now allowing for the mechanical properties of PP, 3D printing opens up more advanced prototyping possibilities. With Polypropylene, 3D printed prototypes meant to achieve high industry requirements can undergo advanced mechanical strength tests, and can offer dependable results.
Lean manufacturing
When it comes to production, 3D printing turns out to be a scalable and very convenient tool for manufacturers seeking flexibility. Whether for 1, 100, or thousands of parts, 3D printing adjusts to your needs without entailing minimum production constraints. This freedom, along with fast turnaround time, make 3D printing best suited for on-demand manufacturing. With such an approach to production, you can address orders and projects as they come, without overburdening stocks or risking waste.
Complex geometries
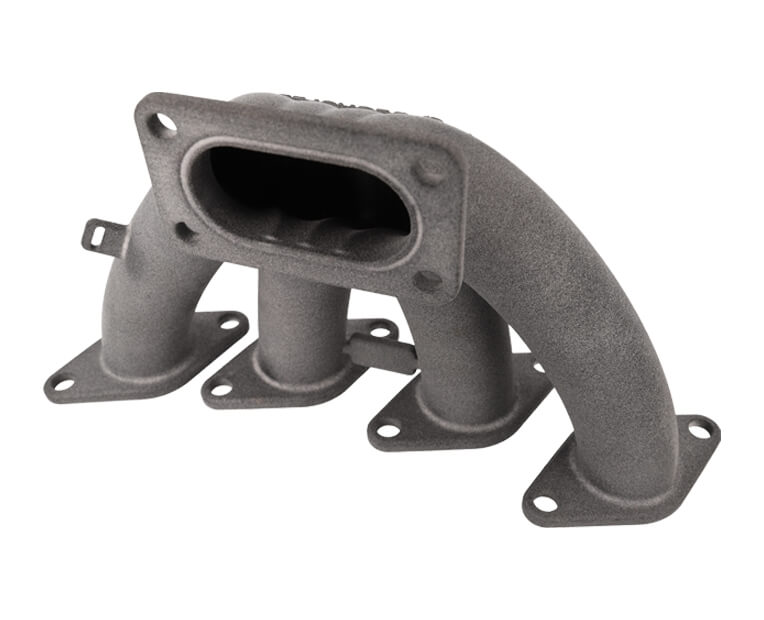
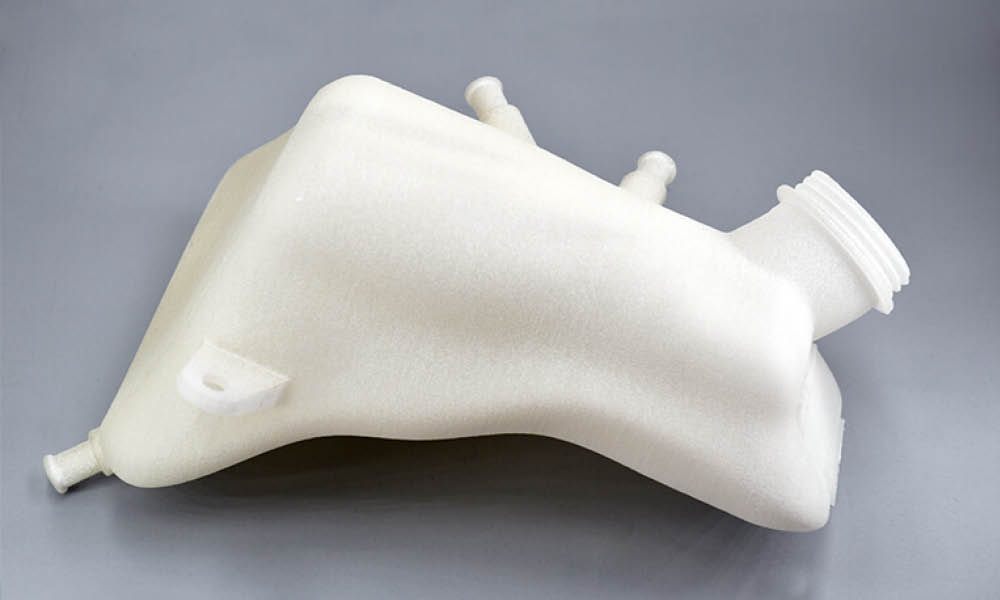
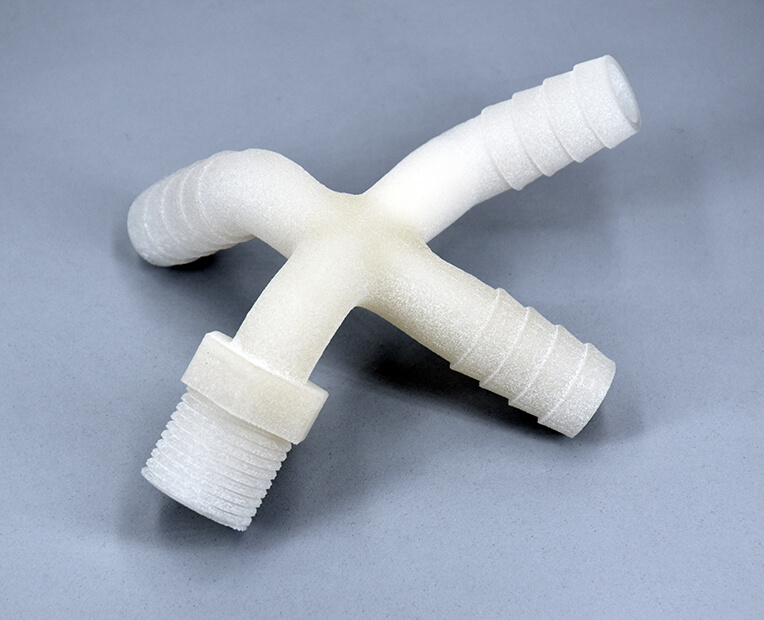
Mechanical systems such as the ones we find in cars tend to imply high technical and spatial challenges. 3D printing and the high design possibilities it relies on can help you answer these.
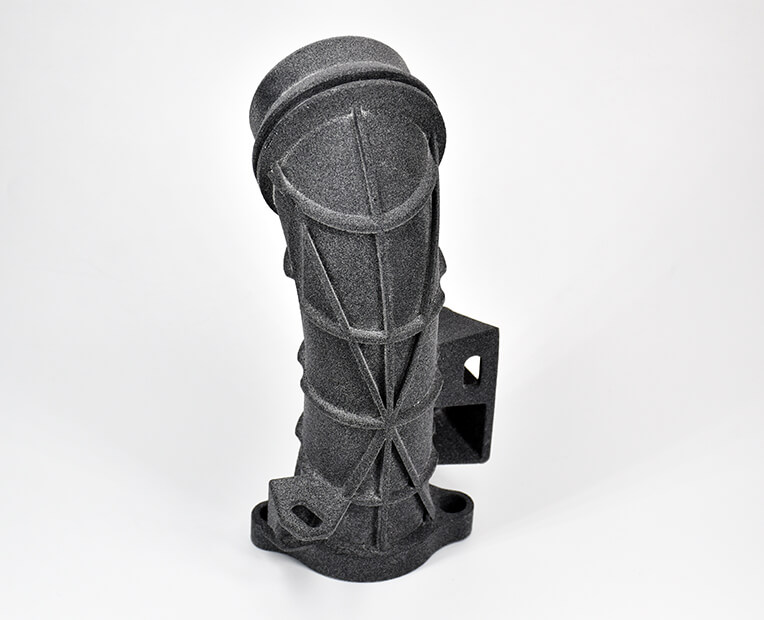
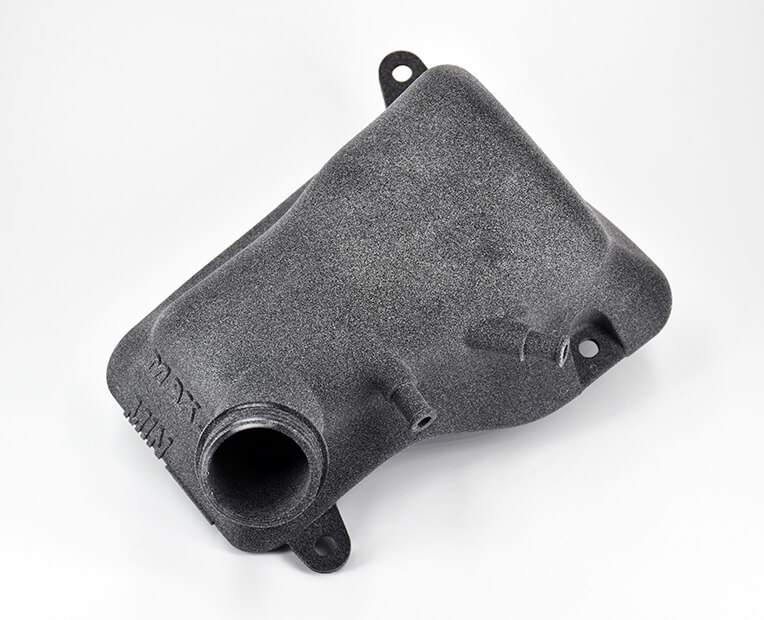
First, the design freedom characteristic of this technology harnesses the potential for more complex shapes. With complex geometries, parts can be best tailored to space constraints and provided with lattice structures, thus optimizing both weight and sturdiness. Depending on the functions that parts are aimed at, better design potential translates to better output. Air and media management parts, for instance, can take advantage of this benefit for optimized flows. With topology optimization tools, part size can be computed and tweaked to spacing issues, so as to achieve the best balance among weight, sturdiness, size, with the least matter possible.
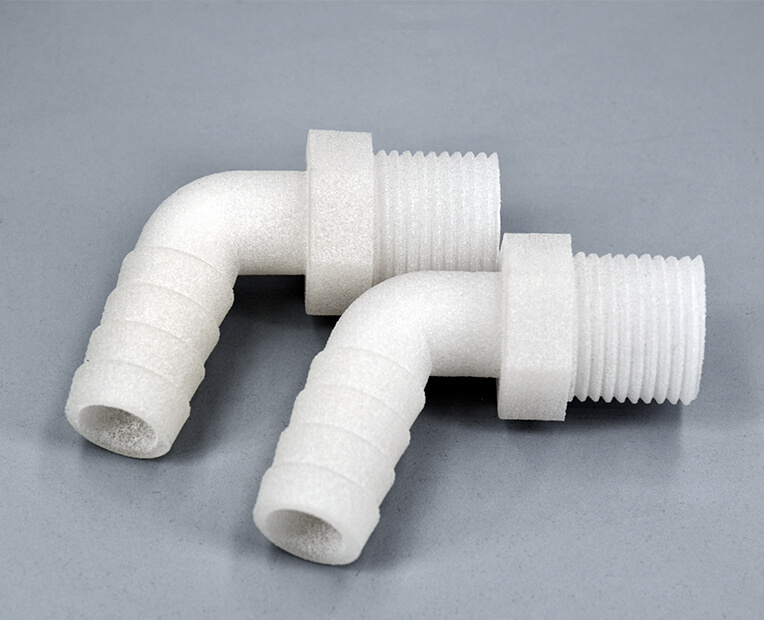
Resorting to PP, parts can achieve a higher complexity, making use of the material’s excellent mechanical properties and the gains offered by Design for Additive Manufacturing.
Customization
Offering the possibility to iterate different designs subsequently, Additive Manufacturing allows to add variations to a single part easily. With parametric design tools, model properties such as wall thickness can be changed only by entering new values. In no time, this approach to design modification allows to tailor unique parts to specific technical constraints.


 Connect with Google
Connect with Google Connect with Facebook
Connect with Facebook